SURGICAL SITE INFECTION
Why is it So Hard to Manage?
Jeremy Shaw, MD
The Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is tranformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.
David L. Rotherberg, MD
The Purgo Pouch stands as a groundbreaking tool in localized antibiotic delivery, addressing deep infection treatment, prevention, and advancing the current surgical infection management. This level of control over drug delivery is a game-changer, and I am excited to see its impact in my clinical work.
Kirt Kimball, MD
Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is transformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.
Jeremy Shaw, MD
The Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is tranformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.
David L. Rotherberg, MD
The Purgo Pouch stands as a groundbreaking tool in localized antibiotic delivery, addressing deep infection treatment, prevention, and advancing the current surgical infection management. This level of control over drug delivery is a game-changer, and I am excited to see its impact in my clinical work.
Kirt Kimball, MD
Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is transformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.

Jeremy Shaw, MD
The Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is tranformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.
David L. Rotherberg, MD
The Purgo Pouch stands as a groundbreaking tool in localized antibiotic delivery, addressing deep infection treatment, prevention, and advancing the current surgical infection management. This level of control over drug delivery is a game-changer, and I am excited to see its impact in my clinical work.
Kirt Kimball, MD
Purgo Pouch is a breakthrough medical device that will deliver controlled local antibiotics. The promise of controlled local drug delivery without systemic side effects and toxicity is transformative for the treatment and prevention of deep infection. I look forward to using it in my practice.

FDA – The State of Orthopedic Device-Related Infections Today
“First of all, once a biofilm forms there is currently NOTHING out there that will eliminate it, other than surgically removing it.”
David W. Lowenberg, MD
Clinical Professor of Orthopedic Surgery
Stanford University School of Medicine
“Continuing to use the same open fracture care tactics we’ve employed for the last 25 years is unlikely to result in different outcomes over the next 25 years. It’s time to change things up”
Michael J. Bosse, MD
Emeritus Professor
Atrium Health Musculoskeletal Institute
“First of all, once a biofilm forms there is currently NOTHING out there that will eliminate it, other than surgically removing it.”
David W. Lowenberg, MD
Clinical Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Stanford University School of Medicine
“Continuing to use the same open fracture care tactics we’ve employed for the last 25 years is unlikely to result in different outcomes over the next 25 years. It’s time to change things up”
Michael J. Bosse, MD
Emeritus Professor
Atrium Health Musculoskeletal Institute
CAUSES OF INFECTION
PLANKTONIC vs BIOFILM
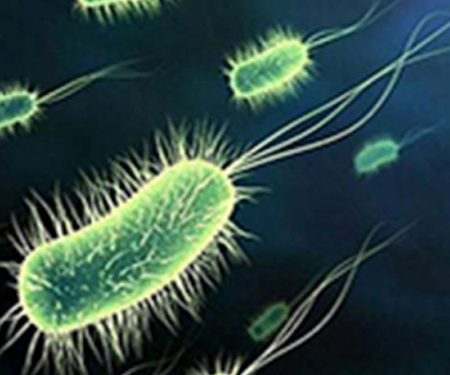
What are Planktonic Bacteria?
- Individual bacteria.
- Float in a liquid medium like blood.
- Metabolically active.
- More susceptible to antibiotics.
- Readily controlled by host immune cells.
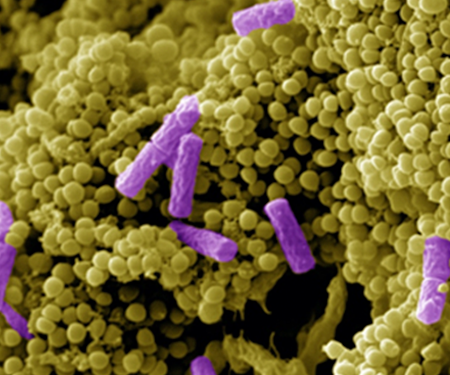
What are Bacterial Biofilms?
- Communities of bacteria.
- Primarily attach to solid surfaces.
- Metabolically inactive
- High tolerance to antibiotics.
- Can cause recurring infections.

What are Planktonic Bacteria?
- Individual bacteria.
- Float in a liquid medium like blood.
- Metabolically active.
- More susceptible to antibiotics.
- Readily controlled by host immune cells.

What are Bacterial Biofilms?
- Communities of bacteria.
- Primarily attach to solid surfaces.
- Metabolically inactive.
- High tolerance to antibiotics.
- Can cause recurring infections.

What are Planktonic Bacteria?
- Individual bacteria.
- Float in a liquid medium like blood.
- Metabolically active.
- More susceptible to antibiotics.
- Readily controlled by host immune cells.

What are Bacterial Biofilms?
- Communities of bacteria.
- Primarily attach to solid surfaces.
- Metabolically inactive.
- High tolerance to antibiotics.
- Can cause recurring infections.
